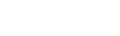slumps
英 [slʌmps]
美 [slʌmps]
v. (价格、价值、数量等)骤降,猛跌,锐减; 重重地坐下(或倒下)
n. (销售量、价格、价值等的)骤降,猛跌,锐减; 萧条期; 衰退
slump的第三人称单数和复数
柯林斯词典
- VERB 急剧下降;暴跌
If something such as the value of somethingslumps, it falls suddenly and by a large amount.- Net profits slumped by 41%...
净利润暴跌了 41%。 - Government popularity in Scotland has slumped to its lowest level since the 1970s.
苏格兰政府的支持率骤跌至 20 世纪 70 年代以来的最低水平。Slumpis also a noun. - ...a slump in property prices.
房地产价格的暴跌
- Net profits slumped by 41%...
- N-COUNT 不景气;萧条;衰退
Aslumpis a time when many people in a country are unemployed and poor.- ...the slump of the early 1980s.
20 世纪 80 年代初的大萧条
- ...the slump of the early 1980s.
- VERB (因疲劳、生病等而重重)倒下,跌倒
If youslumpsomewhere, you fall or sit down there heavily, for example because you are very tired or you feel ill.- She slumped into a chair...
她轰然倒在了椅子上。 - He saw the driver slumped over the wheel.
他看见司机一头栽在了方向盘上。
- She slumped into a chair...
双语例句
- Imports of copper, oil and other commodities have set records as demand slumps elsewhere.
在其它地区需求大幅萎缩的情况下,中国的铜、石油和其它大宗商品进口量均达到创纪录的水平。 - To combat afternoon slumps in enthusiasm and focus, take a walk during the lunch hour.
为了避免一到下午热情和注意力出现骤减,你可以在午餐时间散散步。 - But, in the absence of exchange rate flexibility and in the presence of high interest rates, cutting fiscal deficits on its own may well exacerbate slumps.
但在没有弹性汇率,而利率高企的前提下,单纯削减财政赤字很可能会加重经济低迷。 - On this view booms and slumps are fluctuations around a given trend and any monetary or fiscal stimulus in the downturn must be reversed in the upturn, for example by a budget surplus or a monetary slowdown.
从这种观点看,繁荣和衰退就是围绕着一种给定趋势的波动,同时,低迷时期的任何货币或财政刺激,都必须在上升时期予以逆转比如说通过预算盈余或货币供应减速等手段。 - As the market slumps, homeowners are taking action to stop the build-up of boards.
随着市场的低迷,房主正在采取行动,制止集结板。 - If this adjustment is blocked by weak demand and very low inflation in core countries, the vulnerable countries will be locked into semi-permanent slumps.
如果核心成员国的需求疲软和极低通胀导致调整难以展开,较疲弱的成员国就可能陷入持续时间较长的经济下滑。 - The property market and exports were leading drivers of the booming Chinese economy over the past decade and the slumps in both have taken a heavy toll.
房地产市场和出口是过去10年中国经济繁荣的主要推动力量。这两个市场的暴跌已带来了严重影响。 - Such precipitous slumps are proof that even vast financial resources and powerful brands mean nothing in fast-changing industries.
这些情况表明,在快速变革的行业,即便是巨额财力和强大品牌也无济于事。 - They take the position that fiscal "stimulus" of all kinds is effective against slumps of all causes.
他们认为,无论是应对由何种原因导致的衰退,各类财政“刺激”都是有效的。 - The back of her hair and her veil are lifted, and then she slumps down in the car.
布托背后的头发和面纱都被掀了起来,她突然跌进了车里。